Dic Microscopy Tutorial
Both the microscopes utilize various contrast enhancing. It will not work with plastic.

Molecular Expressions Microscopy Primer Specialized Microscopy Techniques Introduction To Differential Interference Contrast
This interactive tutorial explores optical sectioning in DIC microscopy utilizing a wide spectrum of specimens that differ in thickness.

Dic microscopy tutorial. DIC Microscopy 173 11. We are closely monitoring the situation with COVID-19 coronavirus and following the guidance of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention CDC and federal state and local health authorities. Differential Interference Contrast DIC imaging is a technique used to increase contrast in brightfield images.
Examples of the same specimen viewed in either phase contrast or DIC. Watch the DIC Pre-Training video for the microscope on which youre being trained Nikon Eclipse or TE2000 coming soon. DIC microscopy is a technique which uses gradients in the optical path length and phase shifts to make phase objects visible under the light microscope.
This tutorial is designed to simulate the effects of polarizer rotation on image formation in a Senarmont-compensation differential interference contrast DIC virtual microscope. DIC Differential Interference Contrast. Allows you to view thin transparent specimens at high resolution and high contrast.
The Use of Compensators in DIC Microscopy 167 Comparison of DIC and Phase Contrast Optics 168 Modulation Contrast Microscopy 168 Contrast Methods Using Oblique Illumination 169 Alignment of the Modulation Contrast Microscope 172 Exercise. Trans-illumination modules which condition light on certain models and direct it along the optical path are attached to the support rail of the microscope body via a linear dovetail see. Complete Tutorial 2 Brightfield Microscopy first.
Differential Interference Contrast This tutorial is designed to simulate the effects of polarizer rotation on image formation in a Senarmont-compensation differential interference contrast DIC virtual microscope. Comparison of Phase Contrast and DIC Microscopy. The tutorial initializes with a randomly selected image appearing in the DIC Specimen Image window and a model of an objective and.
Focus and Alignment of Mercury and Xenon Arc Lamps. This tutorial will cover the optical components used in DIC microscopy the basic principles governing how it works and the proper alignment of DIC optical components for the Zeiss Axiovert 200M research microscope. When compared to the typical configuration employed in transmitted light microscopy the critical instrument parameters for reflected or episcopic light differential interference contrast DIC are much simpler primarily because only a single birefringent Nomarski or Wollaston prism is required and the objective serves as.
Need difference in Refractive index. Learn more about the measures we have put in place. FLUORESCENCE MICROSCOPY 177 Overview 177 Applications of Fluorescence Microscopy 178.
Differential Interference Contrast Reflected Light DIC Microscopy. DIC Microscope Component Alignment. In this tutorial the researcher is guided through all aspects of acquiring quantitative confocal microscopy images including optimizing sample preparation for fixed and live cells choosing the.
Phase Contrast Microscope vs Differential Interference Contrast Microscope Phase Contrast and Differential Contrast Microscopes. Example imaging modalities include brightfield differential interference contrast DIC Dodt gradient contrast oblique and darkfield microscopy. Only works with glass.
They have no halo artifacts and relatively thick specimens. In order to operate the tutorial use the mouse cursor to translate the Contrast Mechanism slider between the Phase Contrast Image slider to the extreme left and DIC Image slider to the extreme right positions. In confocal systems DIC images can be acquired simultaneously with fluorescence images and can provide useful morphological information.
Often the compromise between maximum contrast afforded by using smaller apertures is offset by the elimination of interfering specimen features located away from the plane of focus. Phase contrast microscopy and Differential Interference Contrast DIC microscopy are two advanced optical light microscopy techniques to produce high contrast images of unstained and living cells. Interactive tutorial used to optimize pairing of two fluorescent proteins.
Sample preparation can affect DIC. To operate the tutorial use the Polarizer Angle slider to adjust the rotation of the polarizer with respect to other optical components of the system. In this way it is possible to observe living cells and organisms with adequate contrast and resolution.
Differential Interference Contrast DIC Microscopy. The basic optical configuration for differential interference contrast DIC microscopy resembles a traditional polarized light instrument retrofitted with specialized beamsplitting modified Wollaston or Nomarski prisms. Images produced by a DIC microscope are relief-like and seem to have a shadow cast.
Principle DIC microscopy utilizes a system of dual-beam interference optics that transforms local. Examine conoscopic and orthoscopic viewfields in DIC microscopy. In differential interference contrast microscopy wide aperture sizes are useful for optical sectioning experiments where a shallow depth of field is required but high resolution is also necessary.
The relative optical orientation and sequential positioning of the DIC microscope optical components are illustrated in the tutorial as are the wide spectrum of images. As the slider is moved from one contrast mechanism to the other the image changes character and begins to acquire the attributes of the new contrast mechanism. This manual provides instructions for setting up DIC imaging using a laser scanning microscope eg.
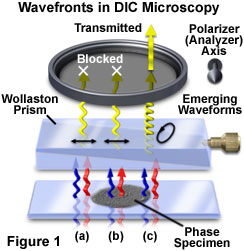
Dic Wavefront Relationships And Image Formation Java Tutorial Olympus Ls

Molecular Expressions Microscopy Primer Specialized Microscopy Techniques Optical Sectioning In Dic Microscopy Interactive Tutorial

