JUST KNOW! Why Do People Form Stereotypes
Society has been socialized into a culture in which race and gender are salient so we unfortunately make judgement based on them. At some point those natural over.

What Role Do Stereotypes Play In American Culture Smithsonian Institution
If fast-food worker came to mind you would be correct.

Why do people form stereotypes. A 1996 research paper 2 suggests that some cognitive and motivational factors positively contribute to the formation application maintenance and change of stereotypical beliefs. 1 In the digital age where rapid and frequent cross-culture communication is a fact of life the reasons why these stereotypes still persist is perhaps more baffling than their origins. Stereotypes are categories of objects or people.
In addition young and old people. Stereotypes of the Japanese as shifty and conniving increased support for their collective internment during WWII. Thus information is more easily identified recalled predicted and reacted to.
Prejudice refers to thoughts and feelings while discrimination refers to actions. Stereotypes are context dependent. Stereotyping means attributing a personality trait or a set of personality traits to a group of people.
There is ample evidence to suggest that negative expectations and stereotypes about the competence of older adults pervade Western culture eg Hummert 1999. March 4 2018 by Hanan Parvez. Between stereotypes objects or people are as different from each other as possible.
Those categories clarify the world for us but they also over-simplify it. In short stereotypes and prejudice are powerful largely because they are important social norms that are part of our culture Guimond 2000. In the absence of the so called total picture to stereotype people in many.
Consistent with Boserups hypothesis historical plough use was found to correlate very strongly with views on gender inequality today. In many cases stereotypes are a shortcut that people use to fill. Picture a high-school dropout.
These stereotypes are so well-known that the. Racism refers to the belief that one race is inherently superior or inferior to other races. People form stereotypes based on inferences about groups social roleslike high school dropouts in the fast-food industry.
Bargh thinks that stereotypes may emerge from what social psychologists call in-groupout-group dynamics. Now think about what occupation that person is likely to hold. All stereotyping is really is a simplified and standardized conception about the characteristics or expected behaviors of an identifiable group.
Stereotyping can also increase a persons sense of in-group identity possibly due to the accentuation principle tajfel and wilkes 1963 that proposes in-group similarities and out-group differences are subconsciously exaggeratedadditionally a negative stereotype held of an out-group will make an in-group appear more favourable and will. Many stereotypes began because of people who are unwilling or unable to get the information they should have in order to make a fair assessment about certain people or situations. For example older adults are characterized as more forgetful and less able to learn new information eg Hummert Garstka Shaner and Strahm 1994.
The way we think creates stereotypes. They are a form of categorization that helps to simplify and systematize information. Because they are so highly cognitively accessible and because they seem so right our stereotypes easily influence our judgments of and responses to those we have categorized.
Stereotypes can help make sense of the world. Categorizing people into groups We think in terms of the categories we create from our experiences. As a result we develop generalized perceptions about people based upon such things as the.
Psychological researchers have sought to identify why certain people employed stereotypes and in much of the twentieth century they were viewed as due to a mental fallacy or misconception of a. Stereotypes are widely circulated oversimplifications of a group of people while generalizations can be based more on personal experience not a widely accepted factor. But towards everyone else its almost human nature to create barriers and form camps around differences.
Stereotyping is considered to be a cognitive process that allows people to associate certain characteristics with a group. In the United States certain racial groups have been linked to stereotypes such as being good at math athletics and dancing. Stereotypes are oversimplified ideas about groups of people.
Humans like other species need to feel that they are part of a group and as villages. Kite and Wagner 2002. This article will focus on the mechanics behind the formation of stereotypes explaining why people stereotype others and how we can begin to break these stereotypes.
We stereotype people when we are unable or unwilling to obtain all of the information we need to make a fair judgement about people or situations. Inparticularwhen types are defined by several dimensions stereotypes are formed along the dimension. Anyone can fall into the trap of ascribing superiority to ourselves at the expense of others.
These traits may either be positive or negative and stereotyping of. We do this because different factors contribute to why people stereotype each other. The process of repeatedly passing social information from person to person can result in the unintentional and spontaneous formation of cultural stereotypes the researchers write in the journal Psychological Science.
So while there may be specific stereotypes like the ones you mentioned which may be true for enough people which is how stereotypes become that way to begin with but the broad stereotype of HAVING stereotypes is true. For instance when comparing Irish to Scots thestereotypeofIrishmaychangefromred-hairedtoCatholic. Appearance posture language and so on.
The assessment of a given target group depends on the group to which it is compared. High-school dropouts are overrepresented in the fast-food industry. Short Answer How do redlining and racial steering contribute to institutionalized racism.

Image Of Typical Welfare Recipient Linked With Racial Stereotypes Association For Psychological Science Aps

These Are The Stereotypes Young People Face When They Come In Contact With The Law The Independent The Independent
Social Categorization And Stereotyping Principles Of Social Psychology 1st International Edition

What Are Gender Stereotypes And How To Stop Them Iberdrola

What Hollywood Movies Do To Perpetuate Racial Stereotypes Film Dw 21 02 2019
11 Stereotypes Prejudice And Discrimination Principles Of Social Psychology 1st International Edition
Our Stereotypes Affect How We Perceive Faces Wired Uk

What Are The Causes Of Stereotypes Getting Race Right

Countering Stereotypes About Asian Americans

How Stereotypes Take Shape Pacific Standard

What Hollywood Movies Do To Perpetuate Racial Stereotypes Film Dw 21 02 2019

What Hollywood Movies Do To Perpetuate Racial Stereotypes Film Dw 21 02 2019

Rigid Gender Roles And Stereotypes Domestic Violence Resource Centre Victoria

Combating Bias And Stigma Related To Covid 19
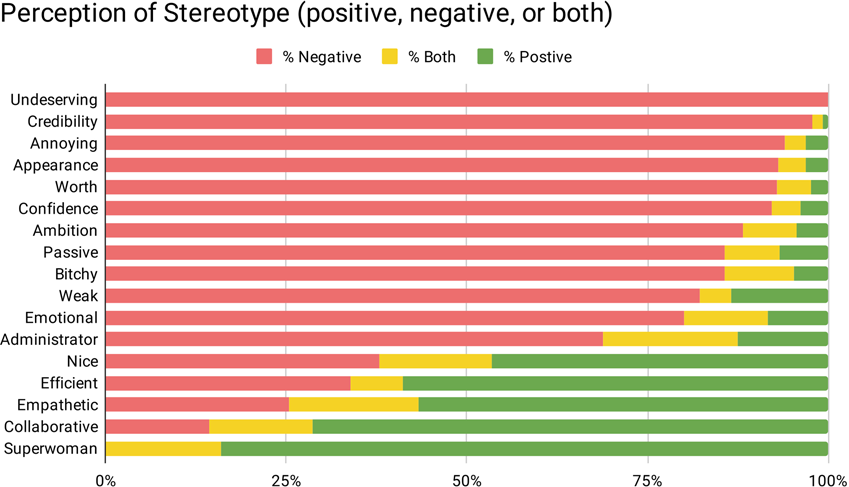
Perceptions Of Stereotypes Applied To Women Who Publicly Communicate Their Stem Work Humanities And Social Sciences Communications

Here S How Pop Culture Has Perpetuated Harmful Stereotypes Of Asian Women

What Hollywood Movies Do To Perpetuate Racial Stereotypes Film Dw 21 02 2019

Rigid Gender Roles And Stereotypes Domestic Violence Resource Centre Victoria
Why Stereotypes Are Harmful Momentous Institute